At Binance.US, your security is our top priority. Over the years, phishing attacks have become increasingly common. Unlike other forms of cyber attacks, phishing attacks involve social engineering, which bad actors leverage to convince, pressure, and persuade targets to give up sensitive information and take actions that put their online accounts and assets at risk.
As phishing attacks become increasingly sophisticated, the best way to protect yourself is to recognize common tactics that bad actors use to gain unauthorized account access and steal funds. To help you recognize common crypto scams, let’s break down some real-time phishing attempts to see how they work.
Fake recruiters on LinkedIn
Imagine getting a message on LinkedIn from someone claiming to be a recruiter. They may have an impressive-looking profile and offer you an exciting job opportunity. This is a common tactic used by scammers to steal your money or personal information. They often advertise remote positions, flexible working arrangements, and attractive salaries. Sometimes, these fake recruiters may even extend job offers without a proper interview.
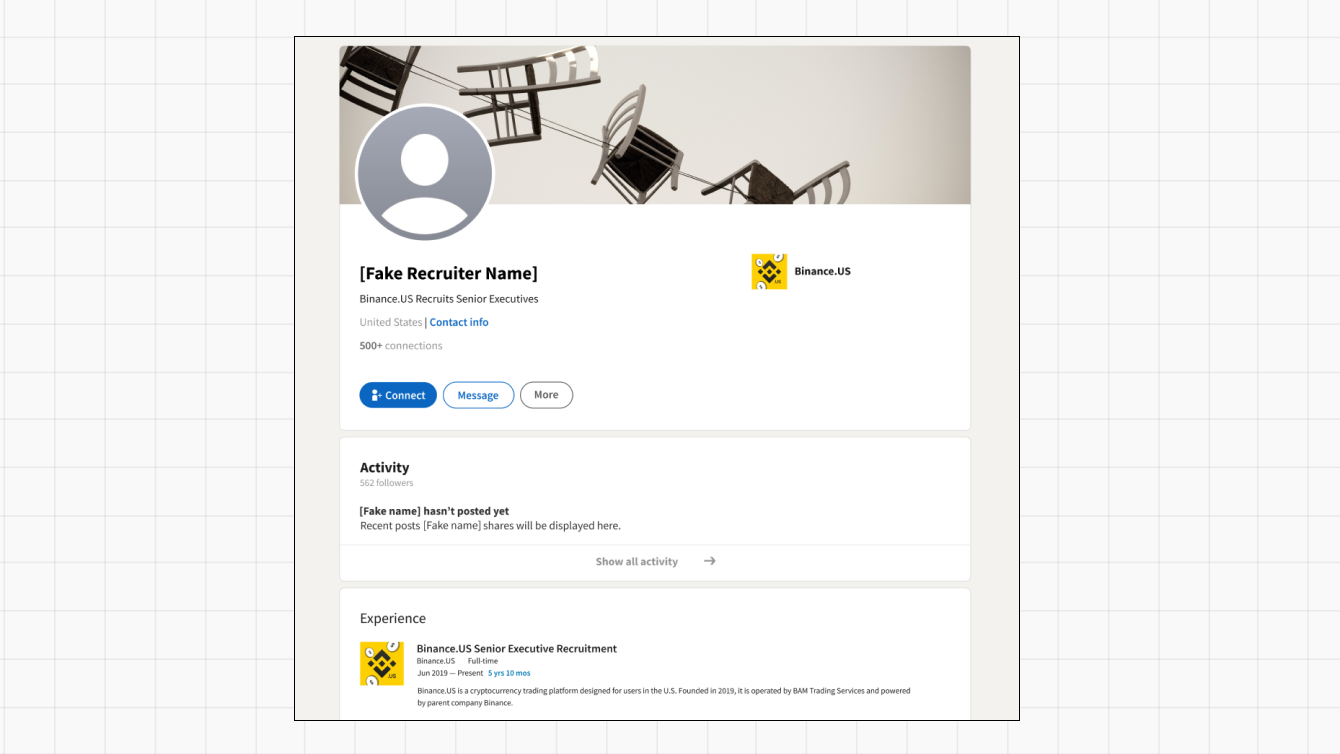
In the example above, someone has created a fake LinkedIn profile to impersonate a “Binance.US Senior Executive Recruitment” team member. Fake recruiter profiles range in sophistication, from simple profiles that contain typos to elaborate ones that feature profile pictures and names of real employees, extensive networks, and other detailed information.
To distinguish real recruitment profiles from fraudulent ones, take care to review the following red flags.
Red flags to watch for
Requests for payment: Legitimate employers will never ask you to pay application or interview fees, download remote desktop software like TeamViewer or Anydesk, or to purchase equipment.
Pressure to act fast: Scammers often try to rush you into making decisions.
Generic communication: Be cautious of recruiters using personal email accounts instead of a company domain.
Requests for sensitive information: Never provide sensitive personal information, such as your SSN or banking information early on in the hiring process. If a job offer requires you to share personal information, like for a background check, double-check that the company and contact are legitimate before moving forward.
Unsolicited interview requests or job offers: Avoid responding to requests for interviews, particularly for roles that you haven’t applied for. If an offer or job sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
How to protect yourself on LinkedIn
In general, it pays to be vigilant whenever you receive unsolicited messages, regardless of whether someone reaches out on LinkedIn or another platform. In this example, a bad actor impersonating a Binance.US recruiter has reached out, unprompted, to a LinkedIn member via direct message.
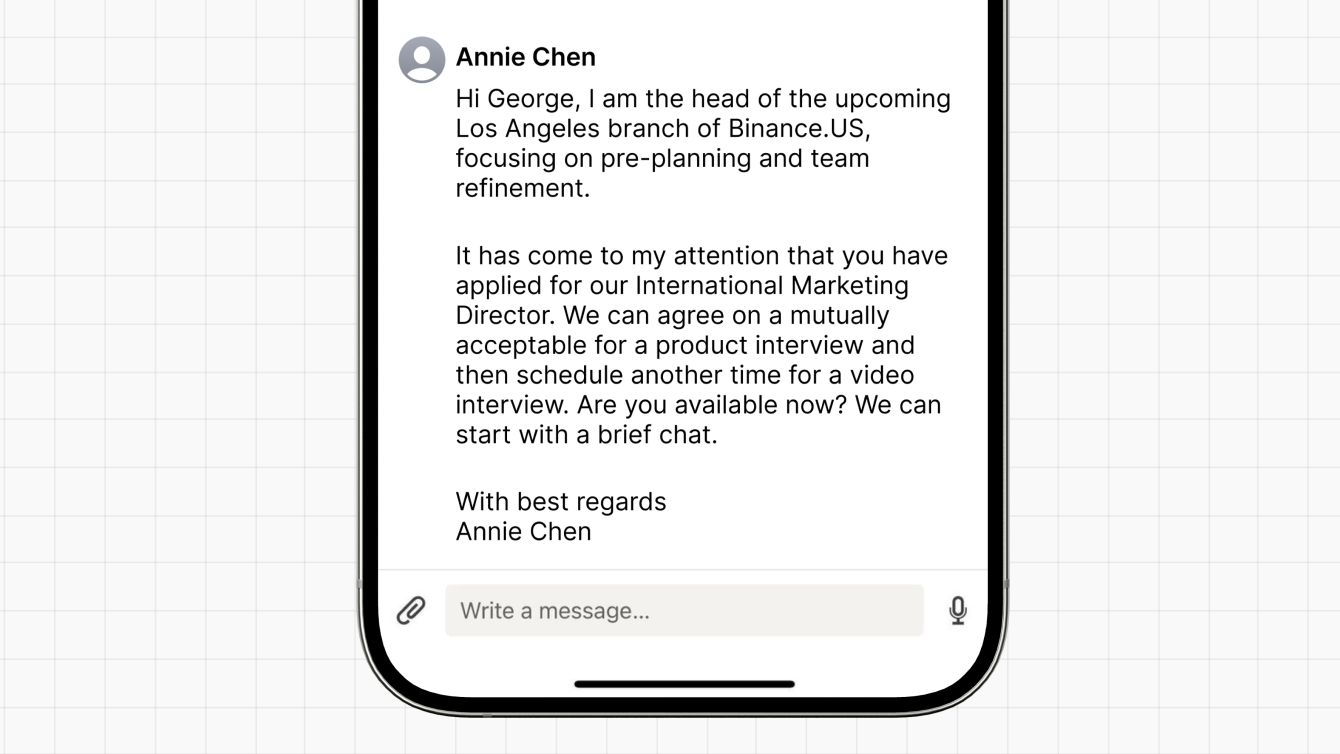
At face value, the message seems innocuous—the only request is for a “productive interview” followed by a video interview. However, there are a few tell-tale signs that this is a scam:
The recipient has never applied for an International Marketing Director role. Furthermore, if the recipient visited our Careers page, they would see that the role does not exist.
The scammer asks whether the LinkedIn member is “available now” for a chat, implying urgency. This provides them with an opportunity to entrap unsuspecting job seekers into a prolonged interaction, where they may apply other tactics to extract personal information and extend the scam.
Had the recipient reached out to Binance.US Support via our official website, they could have verified that both the recruiter’s name, “Annie Chen”, and the “upcoming Los Angeles branch” were fictional details provided by the bad actor.
At Binance.US, we only communicate with candidates through the platform where they initially applied, like our careers page or via our official Binance.US email domain. We will never use platforms like WhatsApp, Telegram, or text message to request interviews or personal information, nor will we use these platforms to share job offer details. Furthermore, we will never ask users to transfer funds, click links, or download software.
If something feels suspicious, do not respond and report the interaction on LinkedIn. In addition, it’s important to avoid downloading any software or clicking on any links included in the message. When in doubt, visit the company’s official careers page or reach out to their support team for confirmation.
Phishing messages
Another common scam involves phishing messages from unknown numbers. While these scams take on many forms, two real-life scenarios we compiled include texts that contain verification codes, also known as One-Time Passwords (OTPs), and texts from bad actors who impersonate an entity you trust.
Fake verification messages
Here’s an example of an unsolicited text message that contains a verification code, or OTP code. It urges the recipient to call a fraudulent phone number if they do not recognize the request.
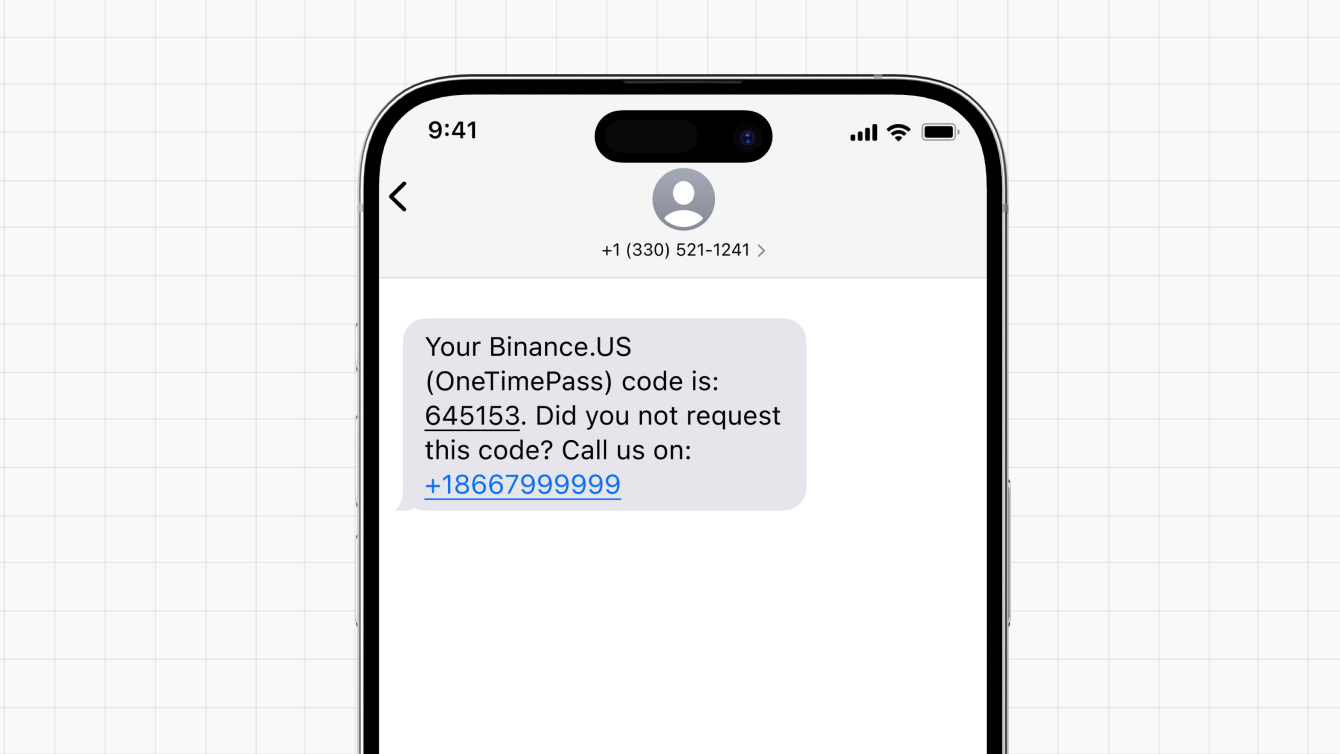
If you receive a verification code that you didn’t request, one of two common scenarios is likely taking place.
You are receiving a phishing message that urges you to call a specific number if you didn't request the code. Once you call the number, a scammer may impersonate an employee and ask you to provide login credentials.
You are receiving a genuine verification code because someone is attempting to log in to your online account(s) with stolen credentials. This may be part of an Account Takeover Attack (ATO), where bad actors attempt to access your online account to steal funds.
Receiving an unsolicited verification code is a major red flag. Never share your codes with anyone and carefully review the message to ensure it is legitimate.
Spoofing and impersonation messages
Spoofing involves disguising the origin of a communication (like an email, phone call, or website) to make it appear as if it came from a trusted source. The following example illustrates a scam message impersonating an automated 'call-back' from a support chat.
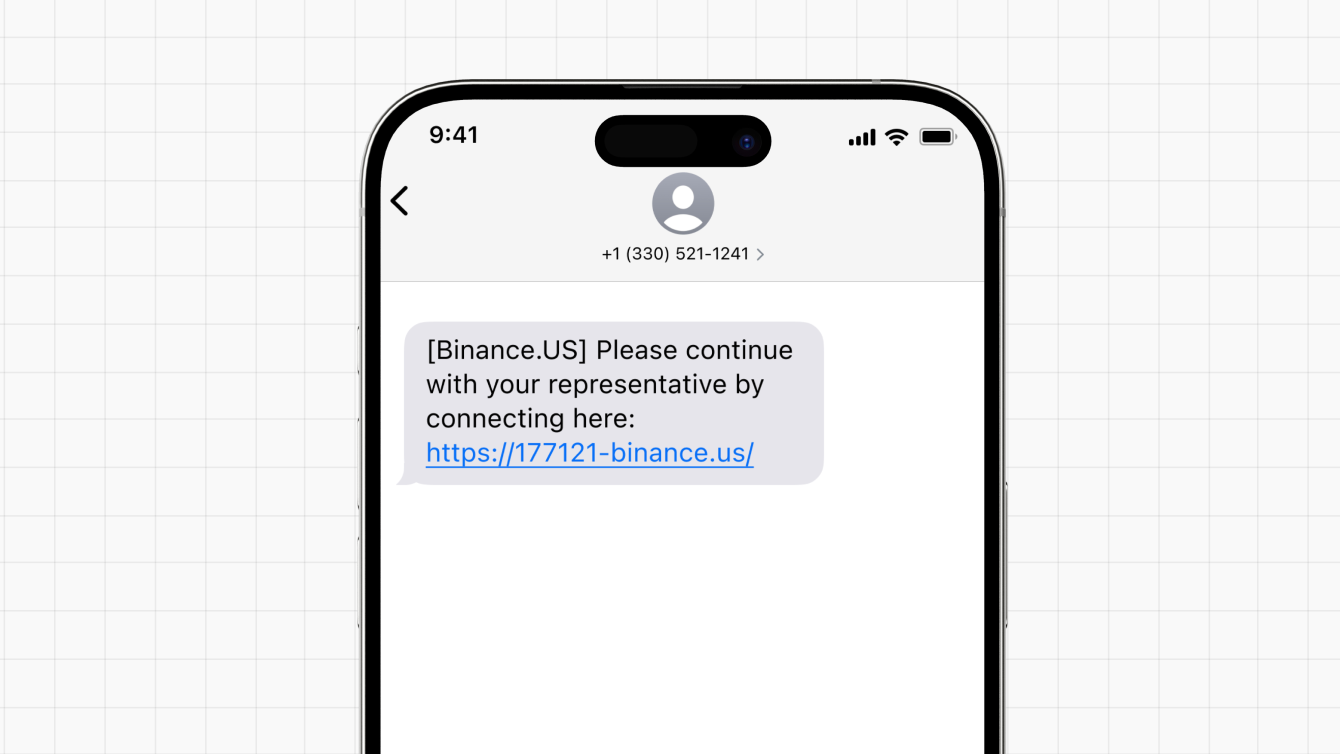
If you receive an unsolicited message from someone claiming to be a trusted entity, such as someone you know, a legitimate business, or a government agency, they may want you to click on a link, download an attachment, or transfer funds. Oftentimes, their messages will use threats or convey a sense of urgency to get you to act quickly.
Red flags to watch for
Unsolicited messages: Receiving an unsolicited message or a verification code you didn't request is always a red flag.
Language conveying urgency: You may receive messages that convey a sense of urgency, such as “Your funds are at risk unless you act immediately”.
Typos and errors: Review messages carefully for grammatical errors or misspellings. If there is a website URL, check it letter by letter to ensure it takes you to a legitimate site. In many cases, bad actors may change a single letter, symbol, or number to make it seem like the link is legitimate.
How to protect yourself from phishing messages
As a rule, avoid responding to unsolicited messages and never share your verification codes with anyone. If a message appears suspicious, promptly report it and block the sender. Always exercise caution with attachments and avoid those from unknown senders. When encountering links, hover over them to inspect the actual URL on a letter-by-letter basis.
If you are unsure whether a message is legitimate, before taking any action, pause to verify the contact through alternate methods, such as directly reaching out to known contacts via trusted channels. Be advised that Binance.US will never call you, ask to be contacted via telephone, ask for your password, or solicit money.
For more information on phishing attacks, including other scams such as romance baiting, giveaway scams, or scam grooming, visit our article on common crypto security risks.
Fake web pages and QR codes
Phishing attacks are increasingly sophisticated, with malicious actors creating convincing fake websites to steal login credentials. These web pages may feature logos, dynamic fields for email and passwords, and even fraudulent QR codes that compromise accounts when scanned.
Red flags for fake web pages and QR codes
Suspicious URLs: Similar to phishing messages, these web pages may be hosted on website URLs that look similar to an authentic website, but may replace a single letter, symbol, or number. Alternatively, they may include unusual domain extensions, such as .xyz, .to, etc.
Generic or poor design: Fake websites often have low-quality graphics, grammatical errors, or an overall unprofessional appearance.
Requests for sensitive information: Be wary of websites that ask for excessive personal information, such as your social security number, bank account details, or passwords
Unexpected QR codes: Be cautious of QR codes from unknown or untrusted sources. They can redirect you to malicious websites or download harmful software.
How to protect yourself from fake web pages and QR codes
When it comes to fake web pages, pay extra attention to how you landed on the page. Did you type in the URL yourself or click on a link? If you clicked on a link, did it come from a trusted source?
As a best practice, always verify the website's URL before clicking links or entering information. Bookmark frequently accessed sites to avoid search engine results that may include paid advertisements for fake websites.
If you see a QR code, verify that it’s legitimate before scanning. If a QR code directs you to a website, ensure the URL aligns with your expectations. When in doubt, manually type the website address into your browser instead of relying on links or QR codes.
Stay ahead of scams
By reviewing these real-life phishing examples, you're now better equipped to identify and avoid phishing attempts. Remember, always double-check the source of any communication and never share sensitive information with unverified parties.
While knowledge goes a long way, be sure to take advantage of all of Binance.US’ built-in security features. Plus, explore more tips to keep your online accounts—and your crypto safe from bad actors.

