This week, we take a look at Celestia, a modular blockchain network tackling the blockchain scalability trilemma through its new blockchain architecture that separates the consensus mechanism from the execution layer.
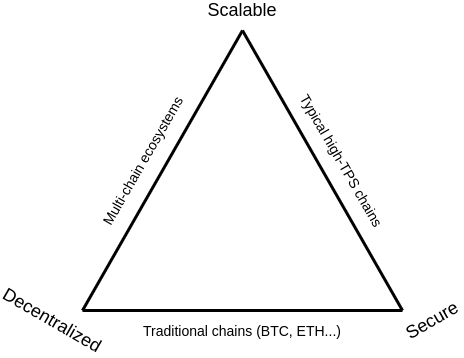
The Scalability Trilemma
As coined by Vitalik Buterin, co-founder of Ethereum, the scalability trilemma addresses the three main pillars of any given blockchain network:
Decentralized: No centralized form of control by a centralized entity.
Scalable: Ability to process an increasing amount of transactions.
Secure: Ability to fend itself against various attack vectors.
Source: Vitalik Buterin
Developers are often forced to make trade-offs between these three main pillars when creating a blockchain. Traditional methods typically only enable developers to achieve two out of three of these properties. For a network that is created to be more decentralized and secure, it will often struggle to scale. The Bitcoin and Ethereum blockchains are some examples of traditional chains that have struggled to scale in recent times, wherein the transactions on these chains will become very expensive whenever network activity increases.
The main reason behind the Bitcoin and Ethereum networks’ inability to scale is because each and every node within both these networks has to process every single transaction. As increased network activity overwhelms the networks’ nodes, a bottleneck will start to form as users fight for blockspace. In essence, there will be too many transactions fighting to be included within the next block (limited space).
To incentivize network security, the Ethereum blockchain allows users to choose to pay higher network gas fees to the miners in order to have their transactions prioritized by said miners. As a result, network gas fees will usually start to increase exponentially during times of network congestion. This causes the network to become more expensive to use, and less accessible to the average user.
As more Decentralized Finance (DeFi) protocols and Non-Fungible Tokens (NFT) projects started building on the Ethereum chain, the Ethereum network became increasingly more congested as more users started to actively utilize the network. This problem gave rise to the creation of alternative Layer 1 blockchains and Ethereum Layer 2 solutions.
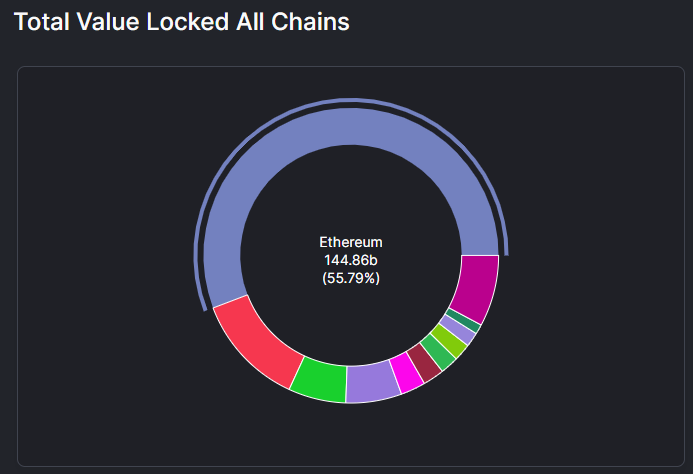
Source: DeFiLlama
The successes of newer, faster and cheaper chains like Terra, Avalanche and Solana effectively gave rise to a multi-chain cryptoverse as network activity spread across multiple networks.
These newer blockchains operate their own set of nodes and validators with their own unique consensus mechanisms. In August of 2020, Ethereum accounted for more than 95% of all the Total Value Locked (TVL) in DeFi. As of the time of writing, Ethereum’s dominance in terms of TVL has fallen sharply to 55.79%. This is largely down to the newer Layer 1 blockchains and Layer 2 scaling solutions cannibalizing its market share.
Celestia
However, most chains today still suffer from the same problem of scalability due to the way that the architectures of their blockchains are designed. Traditional monolithic blockchains like Ethereum run all its processes with shared network resources. This means that all full nodes and validators do everything from execution and consensus, to data availability within the blockchain itself.
Full nodes that validate the chain will need to check for consensus, as well as the validity of network transactions. This architecture inherently inhibits the chain’s ability to scale as full nodes are also required to keep the full history of the blockchain all the way from the genesis block
Enter Celestia.

Source: Celestia
Celestia approaches the scalability problem with a completely new blockchain design. Instead of bundling everything together on the blockchain, Celestia offers a modular architecture where the blockchain’s Consensus and Data Availability Layers are separated from its Execution Layer.
The advantage of decoupling the Consensus Layer from the Execution Layer is that instead of having every node execute all transactions on the blockchain, nodes are now free to execute transactions that are specific to their application(s) of choice.
Typically, traditional blockchains comprise consensus nodes that produce blocks that are then, in turn, verified and authenticated by full nodes and light nodes. By this design, full nodes are supposed to store the entire history of the blockchain. As a result, operating a full node will increasingly become more expensive over time as the blockchain’s data inevitably grows over time.
This creates a scalability bottleneck where the number of full nodes will decrease as there will come a point in time when they can no longer be run on regular consumer hardware. Concomitantly, this will result in a centralization of the network as larger and wealthier node operators start to take control of a larger share of the blockchain.

Source: Celestia
By separating the Consensus and Data Availability Layers from the Execution Layer, Celestia is able to achieve unprecedented levels of scalability with their novel Data Availability Sampling (DAS) technology.
Without diving too deeply into the granular technical details, DAS is a probabilistic guarantee that enables light nodes to prove consensus by relying on fraud proofs from full nodes without the need for downloading the whole blockchain, all while retaining an equal or similar level of security as a full node. With DAS, blocks can be safely made bigger as more light nodes are empowered to participate in the network. This will enable the network to scale more as larger blocks allow for a larger number of transactions.
Latest Developments
While Celestia is still in early development, the team behind Celestia recently launched the Celestia Devnet in December of 2021. The devnet was successfully launched with a group of 7 Celestia validator nodes and 4 full nodes and light nodes that were able to create blocks and sync block headers (whilst carrying out data availability sampling concurrently) respectively.
Source: Celestia Launches Devnet
Currently, the devnet houses three core components that include the chain’s consensus and networking mechanism, the state machine that processes and handles transactions, as well as Optimint, a software that allows a Cosmos zone to deploy directly onto Celestia as a rollup.
You are able to observe the live devnet through its block explorer. The team plans to launch its public testnet in 2022.
In addition to its devnet, Celestia recently introduced its Quantum Gravity Bridge, a secure off-chain data availability solution for Ethereum Layer 2s.

Source: Celestium
Although Ethereum Layer 2 solutions aim to make Ethereum more scalable whilst preserving its decentralization and security, the rollups themselves have faced their fair share of issues due to rising gas fees and an influx of activity.
Celestia’s Quantum Gravity Bridge serves as a scalable off-chain data availability solution using Celestiums, an Ethereum Layer 2 chain that utilizes Celestia for data availability, but leverages Ethereum for settlement and dispute resolution.
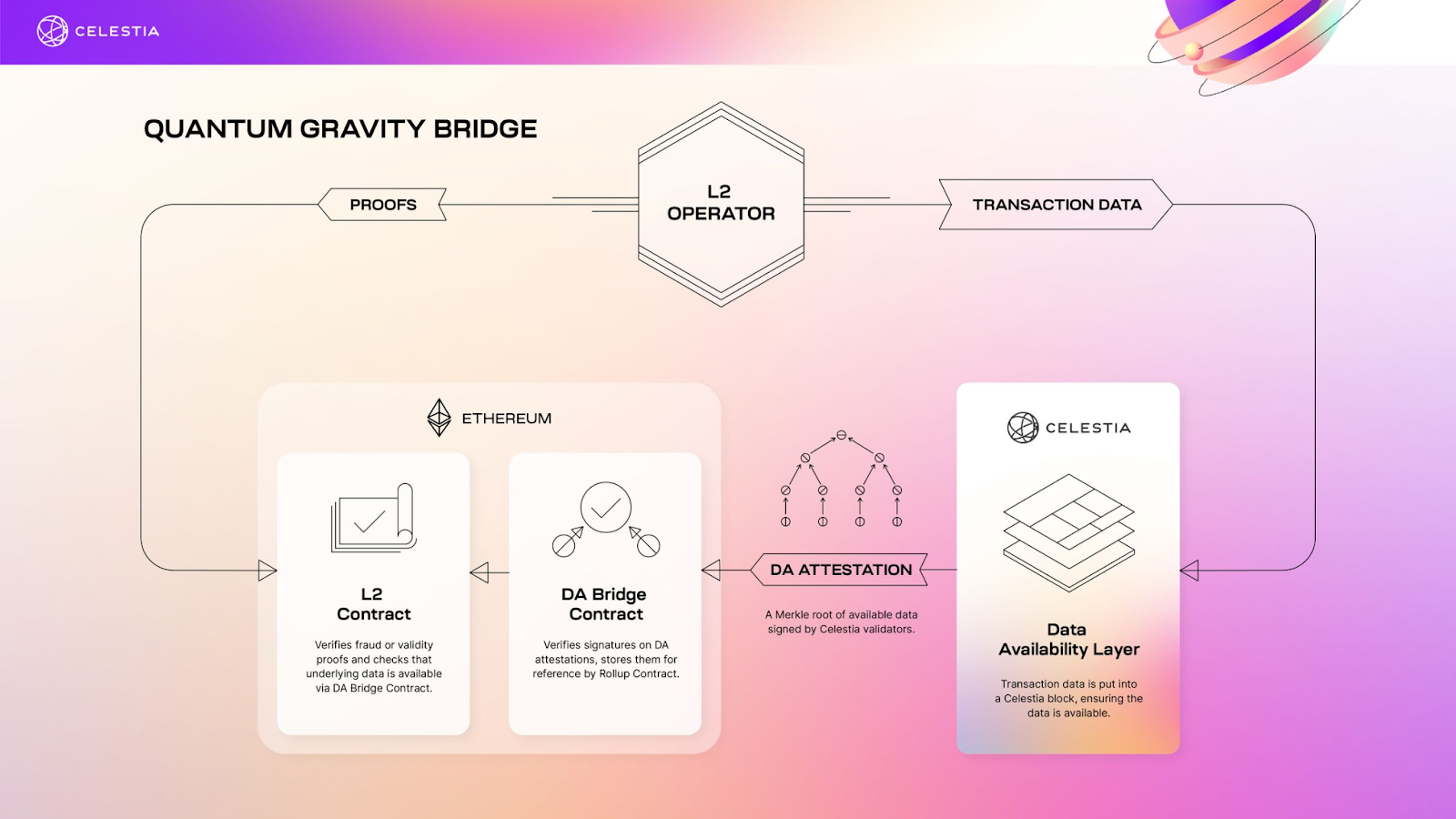
Source: Celestium
In essence, Celestium provides an interesting combination of security and scalability by leveraging on Celestia’s high throughput data availability while still retaining a higher level of security than other off-chain data availability techniques. This effectively allows for better scalability.
Although still early in its development, Celestia looks to be a promising attempt at solving the scalability trilemma with its new and innovative modular blockchain architecture. In theory, this design improvement will enable Celestia to achieve much greater levels of scalability, flexibility and interoperability than its predecessors.
We will be keeping a keen eye on this one.
Disclosure: Members of Bybit may be invested in some or all of the tokens and projects mentioned within the following article. This statement discloses any conflict of interest and is not a recommendation to purchase any token or participate in any of the mentioned ecosystems. This content is purely for educational purposes only, and should not in any way be construed as investment advice. Please exercise caution and practice your own due diligence if you are planning to partake in any of these projects in any way.

