This week, we take a brief look at Celestia, a modular Layer 1 proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain. In this article, we dive into its architecture and ecosystem, and comment on our findings.
Preface
Blockchains have evolved over the years, with each iteration trying to solve the blockchain trilemma of decentralization, scalability, and security. Blockchains like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana are monolithic in structure and have four core functions; data availability, consensus, settlement, and execution. However, monolithic blockchains inevitably run into scalability issues due to the fact that all of these functions compete for the same resources.
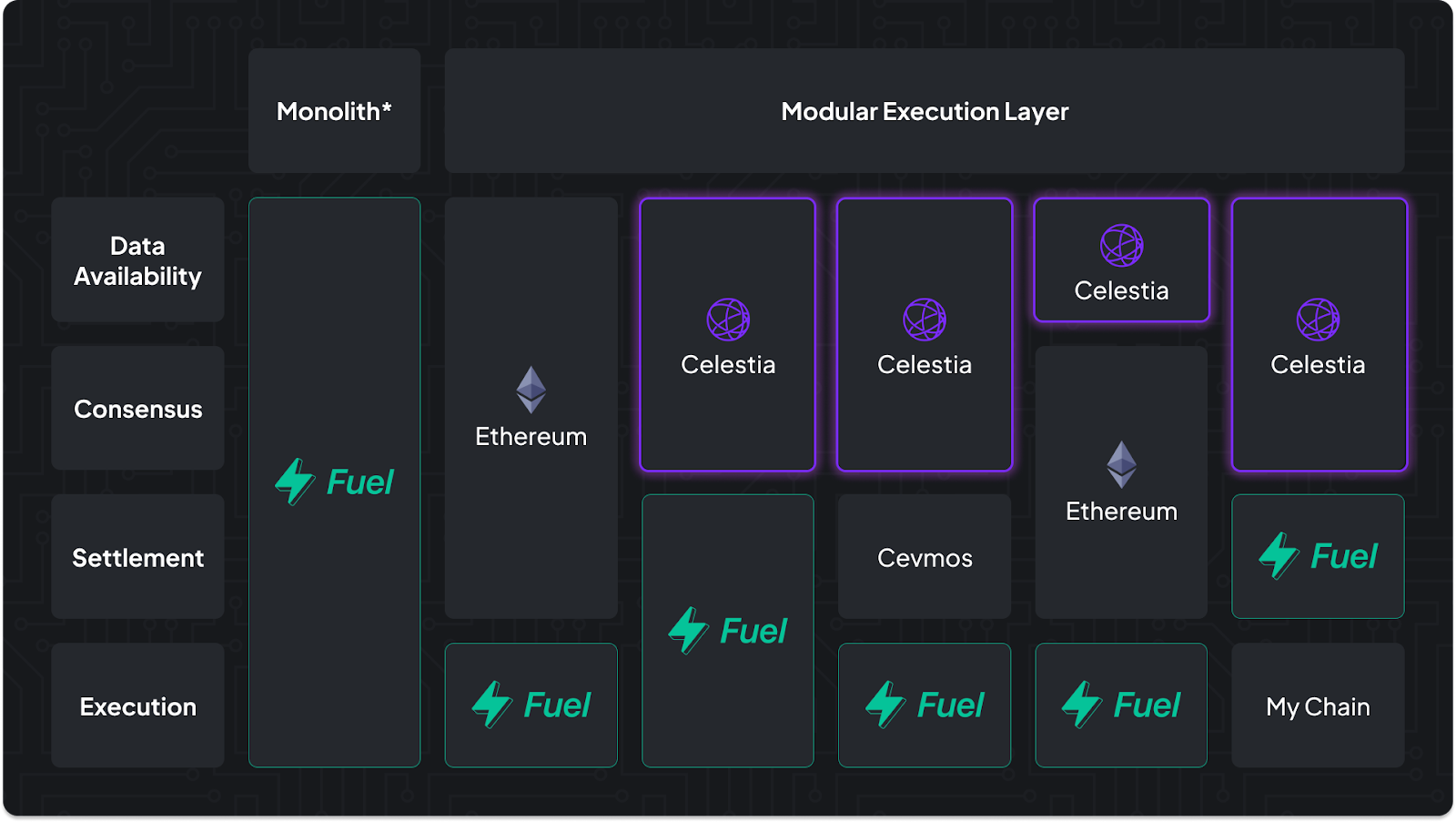
Source: Fuel Labs
On the other hand, modular blockchains like Fuel and Celestia separate these functions into multiple layers, as seen above.
What is Celestia?
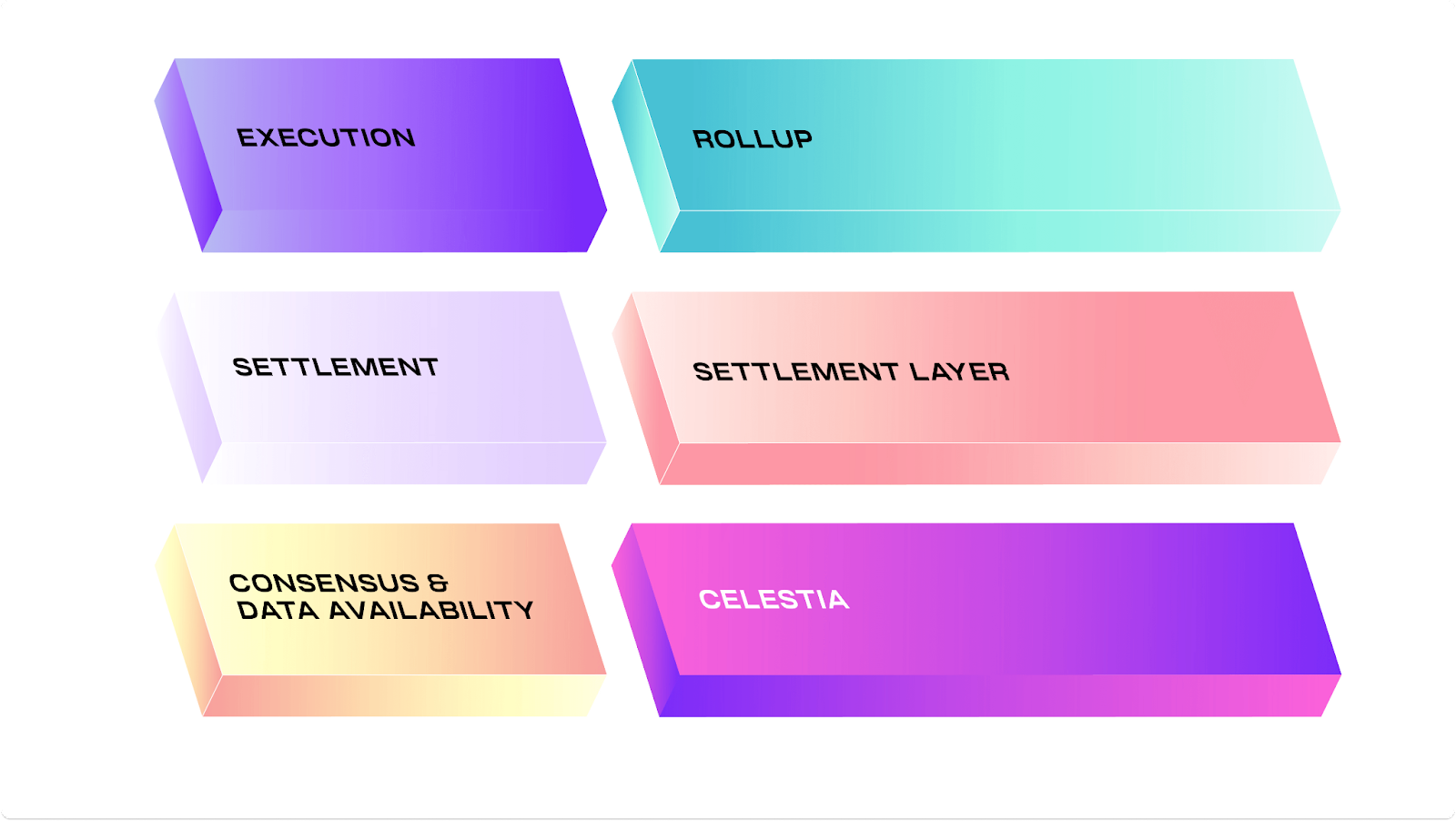
Source: Celestia
Celestia (formerly LazyLedger) is a modular Layer 1 proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain that decouples the execution and validity functions from the consensus layer. This means that its only function is to order transactions and guarantee its data availability without having to worry about execution and transaction validity, thus making it highly scalable. Developers can build optimized and customized blockchains or rollups on top of Celestia to leverage its shared security layer, which uses Tendermint as its consensus engine.
Data Availability
The data availability problem concerns the ability to verify that all data is available and transparent for the entire node network when a new block is produced. Each block is composed of two parts: a header which contains the metadata of the block and transaction data which makes up the majority of the block. In a typical blockchain network, there are two types of nodes:
Full nodes— downloads and verifies every transaction on the blockchain. Demands a lot of resources and storage space but are the most secure type of nodes.
Light clients— downloads only the block header, does not download or verify transactions. Less secure than full nodes.
For example, Ethereum, which is a monolithic blockchain, guarantees data availability by depending on full nodes which download entire blocks. Although this approach is the most secure and removes any possibility of a double-spend transaction, this limits its ability to scale. This has resulted in its dependence on rollups, both zero-knowledge ( ZK-rollups) and optimistic based, as a long-term solution.
On the other hand, Celestia supports multiple types of nodes, each with a specific role on the network.
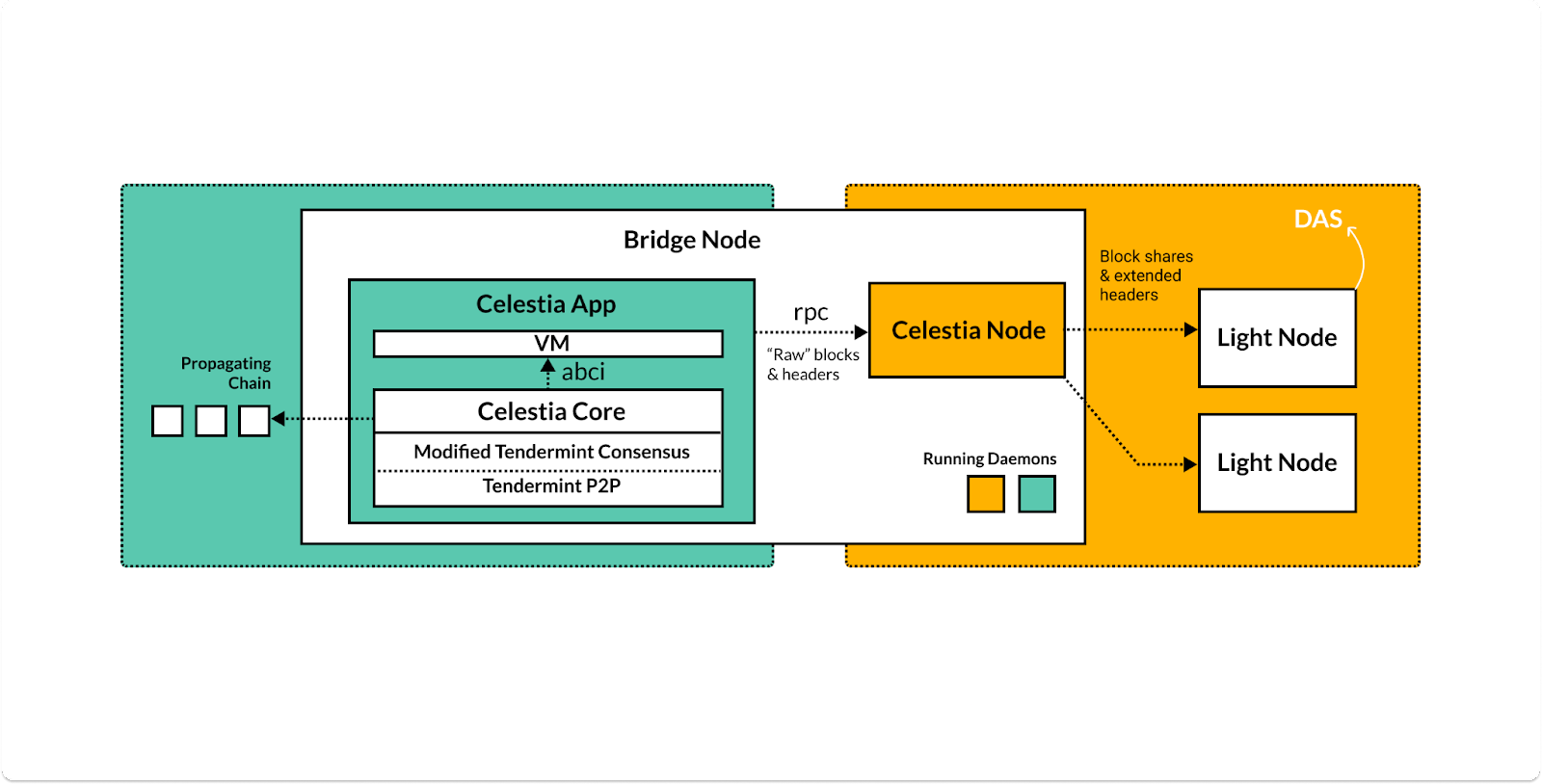
Source: docs.celestia.org
Consensus Nodes
Validator Node — participates in consensus on the Celestia network
Consensus Full Node — syncs blockchain history in Celestia’s consensus layer
Data Availability Nodes
Bridge Node — connects the data availability and consensus layers, while having the option of becoming a validator node
Full Storage Node — stores all data on the network, but does not connect to Celestia App
Light Node — ensures data availability and performs data availability sampling (DAS) on the data availability network
Because Celestia does not need to worry about transaction validity, block verification only needs to handle data availability verification. This is done via data availability sampling (DAS), which allows users (light clients) to verify availability by sampling small random chunks without needing to download the entire block.
Fraud Proofs
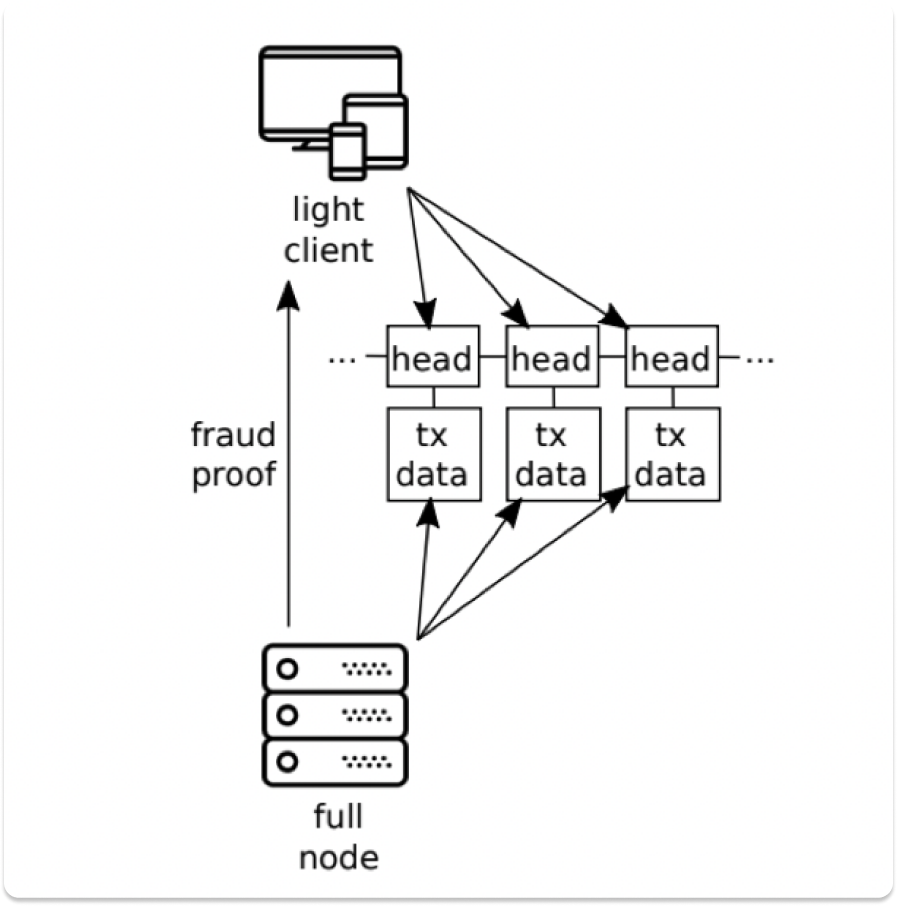
Another key reason that Celestia can use light clients is because they are able to detect invalid transactions from the DAS process via fraud proofs. Light clients rely on full nodes to send fraud proofs and are thus able to detect invalid transactions without knowing the state of the entire blockchain.
As more light nodes join the network to sample the entire block, block size increases without sacrificing security or decentralization. Monolithic blockchains would have had to sacrifice decentralization because bigger block sizes would increase hardware requirements for nodes to download and verify data. Furthermore, because rollups also depend on data availability to scale, increased scaling on Celestia would mean better scaling potential for the rollups utilizing Celestia.
Roadmap
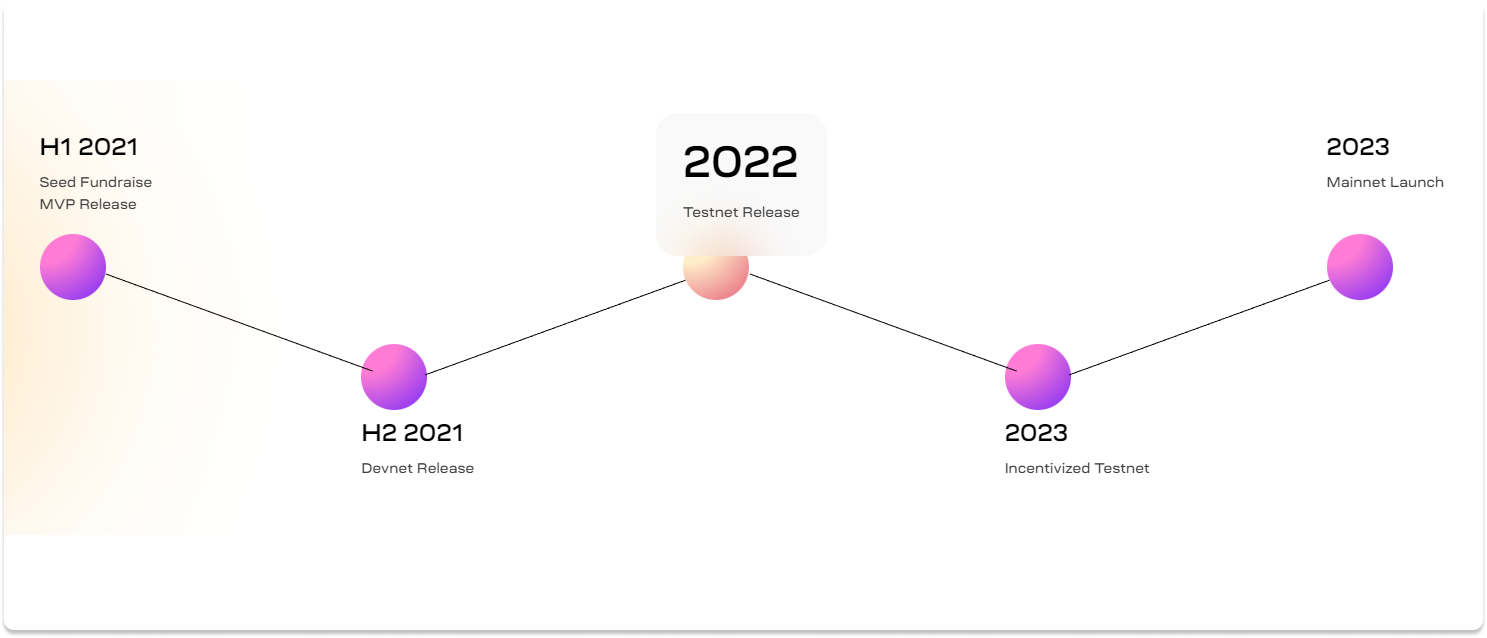
Source: celestia.org
On May 25, 2022, Celestia launched its testnet, named “Mamaki”, featuring a data availability API which enables developers to submit data for a namespace and retrieve data by namespace from Celestia. Developers will also be able to build Cosmos SDK rollups using Optimint as the ABCI client, although fraud proofs are not yet available. In the future, Celestia plans to enable developers to use Celestia to deploy EVM based rollups and as a data availability bridge for sidechains and validiums.
Community members looking to get involved in the testnet are able to operate nodes, receive testnet tokens from the faucet, delegate to and undelegate from validators, and send transactions between wallets. However, it is worth noting that the current testnet is not incentivized — incentivized testnet will launch closer to mainnet in 2023.
Team & Backers
Celestia was founded by Mustafa Al-Bassam, Ismail Khoffi, and John Adler. Al-Bassam holds a PhD in blockchain scaling and co-authored a paper on fraud and data availability proofs alongside Vitalik Buterin. Adler, is also the co-founder of Fuel, a modular blockchain execution layer, which we covered here. The founders of Celestia have all had ample experience in building and scaling blockchains, in addition the Celestia team is composed of engineers with experience in Google, AWS, Oracle, and other blockchain projects like Ethereum and Cosmos.
In terms of funding, Celestia closed a seed round of $1.5 million back in 2021, with participation from Interchain Foundation, Binance Labs, and Maven 11, among others.
Final Thoughts
In our deep dive into Fuel, we concluded that modular blockchains would see increasing adoption due to Ethereum’s roadmap focusing on rollups for scaling in the foreseeable future before sharding is implemented. However, modular blockchain architecture is still nascent and we are yet to see them implemented at scale.
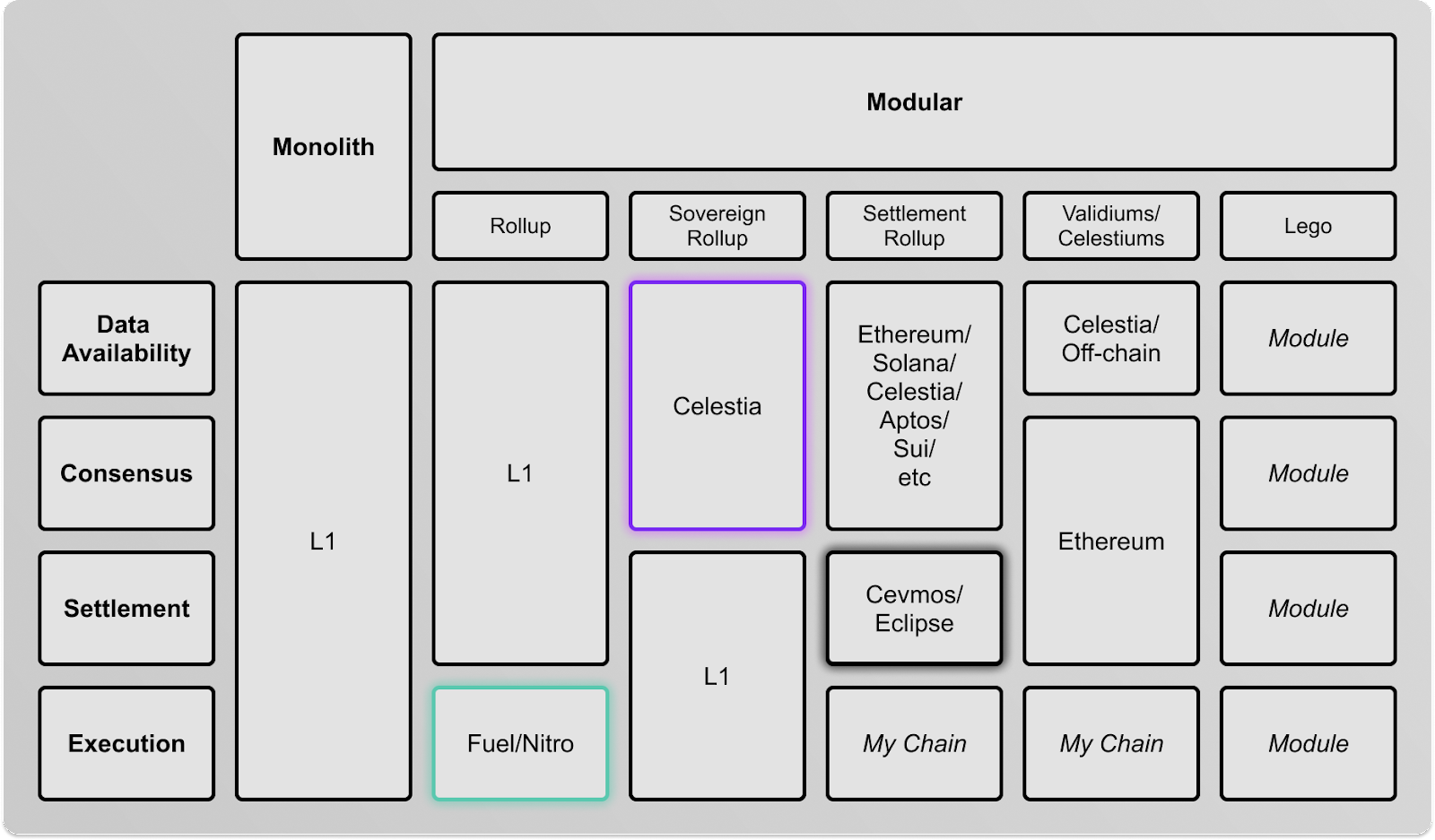
Source: @cryptoian , via Twitter
Modular blockchain solutions like Celestia, Fuel, and Nitro give developers a wide range of options to not only scale blockchains, but to enable cross-chain interoperability as well. Jon Charbonneau of Delphi Digital details here a number of ways that Celestia could be utilized, as a base layer providing data availability, as a Cevmos settlement rollup, or as EVM-based rollups (illustrated above). The real test however, would be to see how all this plays out in reality — we think that the future is one that involves a multitude of modular app-specific or purpose-specific chains that are both scalable and interoperable. This is already apparent in the Cosmos ecosystem, where teams are leveraging the interoperability and customizability of Cosmos architecture to build appchains. With modular architecture like Celestia, teams have even more options to scale and design their blockchain architecture. It will certainly be exciting to see what transpires as Celestia moves towards mainnet and as developers start to utilize it.
Disclosure: Members of Bybit may be invested in some or all of the tokens and projects mentioned within the following article. This statement discloses any conflict of interest and is not a recommendation to purchase any token or participate in any of the mentioned ecosystems. This content is purely for educational purposes only, and should not in any way be construed as investment advice. Please exercise caution and practice your own due diligence if you are planning to partake in any of these projects in any way.
Referenced Articles:
Progression of the Data Availability Problem

