
What is staking?
Staking is a process in which holders of certain types of cryptocurrencies can earn rewards by participating in the transaction validation process in Proof of Stake networks.
In order to participate in staking, a user must have a certain amount of the stakeable coin in their wallet and must run a node on the network. The node validates transactions and helps to secure the network by adding new blocks to the blockchain, and is rewarded in kind.
Staking can be an attractive option for cryptocurrency investors because it allows them to earn passive income by simply holding and supporting the network, rather than buying and selling the cryptocurrency on an exchange. It also helps to improve the security and decentralization of the network by distributing the validation process among a larger number of users.
Some examples of stakeable coins include Cosmos (ATOM), Solana (SOL), and Near (NEAR). The specific requirements for staking and the rewards earned may vary depending on the cryptocurrency.
Proof of stake
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a consensus mechanism whereby validators commit a certain amount of a platform’s native token as collateral in order to validate blocks and receive a reward. It disincentivizes malicious or dishonest actors through punishments like slashing events in which validators can lose their stake.
This sort of mechanism can be contrasted with Proof of Work (PoW) which relies on miners to solve complex mathematical problems in order to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain for a reward. In this system, the miner with the most computing power has the best chance of being chosen to validate the next block.
In a proof of stake system, the user who holds the largest stake of the cryptocurrency is typically chosen to validate the next block. The probability of a user being chosen to validate a block is proportional to their stake in the cryptocurrency. For example, if a user holds 10% of the total stake in the cryptocurrency, they have a 10% chance of being chosen to validate the next block.
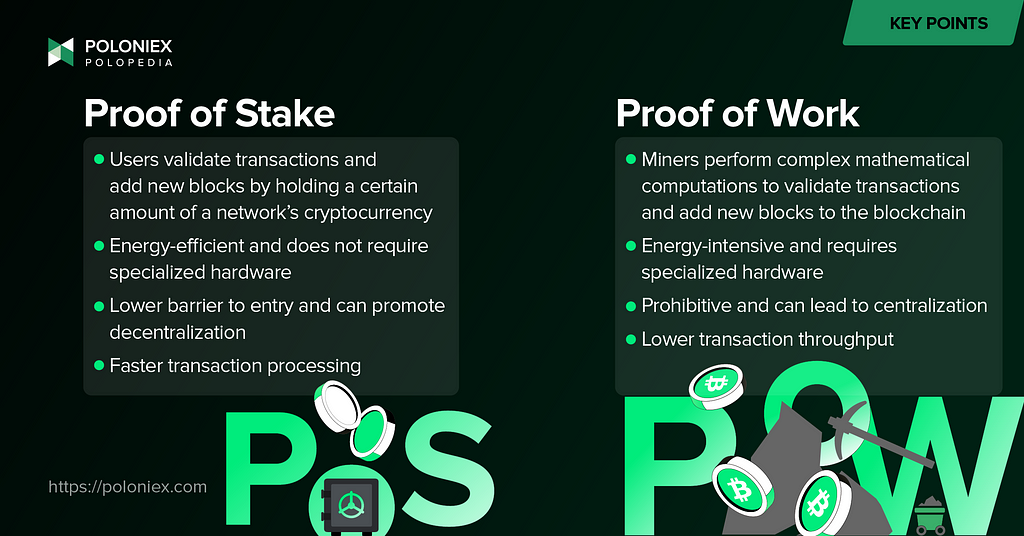
Advantages of Proof of Stake
There is much debate over what the superior consensus mechanism is, especially between PoS and PoW. Proponents of PoW cite its resistance to centralization due to the fact that one cannot simply buy up a majority of a token’s circulating supply and retain the overwhelming majority vote on any proposals or, in the worst of cases, be able to act maliciously and commit a 51% attack on a network.
Energy efficiency: One of the main advantages of proof of stake is that it is much more energy-efficient than proof of work (PoW). In a PoW system, miners must perform complex mathematical computations in order to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. This requires a lot of electricity, which can be costly and can also have negative environmental impacts. In contrast, proof of stake does not require users to perform any computations, so it consumes much less energy.
Greater decentralization: Another advantage of proof of stake is that it can help to promote decentralization. In a PoW system, the miners who operate specialized hardware often have a disproportionate amount of influence on the network. This can lead to a more centralized network. In contrast, proof of stake allows a larger number of users to participate in the validation process, which can help to distribute power and influence more evenly.
Faster transaction processing: Because proof of stake does not require users to perform complex mathematical computations, it can be faster than PoW at validating transactions. This can lead to faster transaction processing times and less network congestions. And with networks that utilize shardchains alongside a PoS engine, they can achieve even greater transaction throughput.
Lower barriers to entry: Proof of stake is also regarded as having lower barriers to entry than PoW. To participate in the mining process in a PoW system, users typically need to invest in specialized hardware and a significant amount of electricity. In contrast, proof of stake only requires users to hold a certain amount of the cryptocurrency, which can be more accessible for a wider range of users. All you need is a computer, a reliable internet connection, and a network (or exchange)-specific minimum amount of the cryptocurrency to start staking.
However, there are a few potential disadvantages of using a proof of stake (PoS) consensus mechanism for a blockchain:
Centralization risk: In a proof of stake system, the users with the largest stakes have the greatest influence on the network. This can lead to a concentration of power among a small group of users, especially in setups like Delegated Proof of Stake systems. This might result in a more centralized network, meaning an outsized influence of these members as well as vulnerability to a 51% attack.
Distribution issues: Similar to the centralization risk, a PoS system can succumb to more centralization early on when the token supply distribution is not properly planned out. If a group of early investors secures an outsized proportion of the total supply, this can pose legitimacy and governance issues.
How are staking rewards determined?
Annual percentage yield (APY) is a measure of the rate of return (the yield) on an investment over a year (that’s the ‘annual’ part), expressed as a percentage. In the context of staking crypto on a centralized exchange, APY refers to the percentage of return that a user can expect to earn on their staked cryptocurrency over the course of a year. It is listed besides the specific token, and every token has a different APY.
APY is calculated by taking into account the amount of the cryptocurrency staked, the staking rewards earned, and any fees or other costs associated with the staking process. It is important to note that the actual APY earned may vary depending on a number of factors, including the performance of the cryptocurrency, changes in staking rewards or fees, and other market conditions.
In terms of rewards distribution, staking rewards are typically distributed to users who participate in the staking process on a regular basis, such as daily or weekly. The amount of the reward earned by each user is typically proportional to their stake in the cryptocurrency. For example, if a user holds 10% of the total stake in the cryptocurrency, they may earn 10% of the total staking rewards for each block they help to validate. With Polo, rewards are distributed every day based on a snapshot of a user’s Earn account balance.
Staking on your own vs staking with an intermediary
Today, there are many options one has when choosing how to go about participating in the validation process and securing a distributed network through staking. On one hand, you can go through the process of setting up a validator. While this will give you the highest rewards, it takes technical know-how as well as a higher minimum amount to participate in the validation process. There are also the risks of, if you’re validator is faulty, slashing risks, or missing out on rewards.
On the other hand, there are intermediaries like Poloniex and other exchanges that offer staking. These solutions require little to no technical knowledge, although rewards rates will be lower. The nice thing about staking through an exchange like Poloniex is that it also helps mitigate slashing risks and offers a very easy-to-use experience with minimal steps.
How to stake on Poloniex
Staking on Poloniex is quite simple thanks to our one-step opt-in experience.
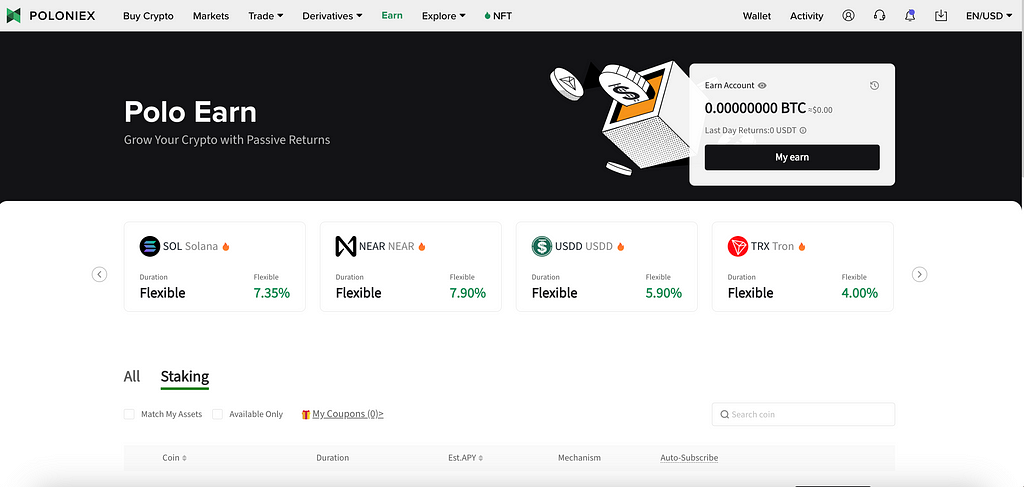
Just navigate to the earn page from the menu bar on our homepage.
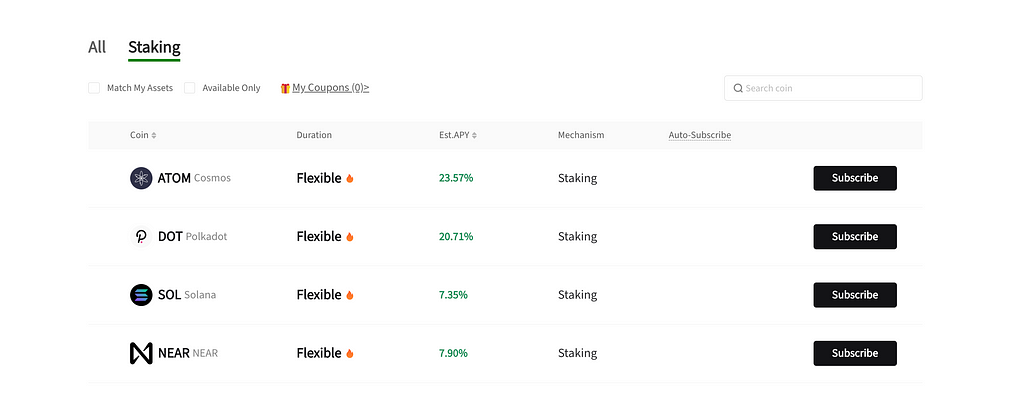
After that, click on the Staking section and you will see the available cryptocurrencies listed out below! Today, we’re going to stake some ATOM. Click ‘Subscribe’ and a popup will appear asking you how much you want to stake👇
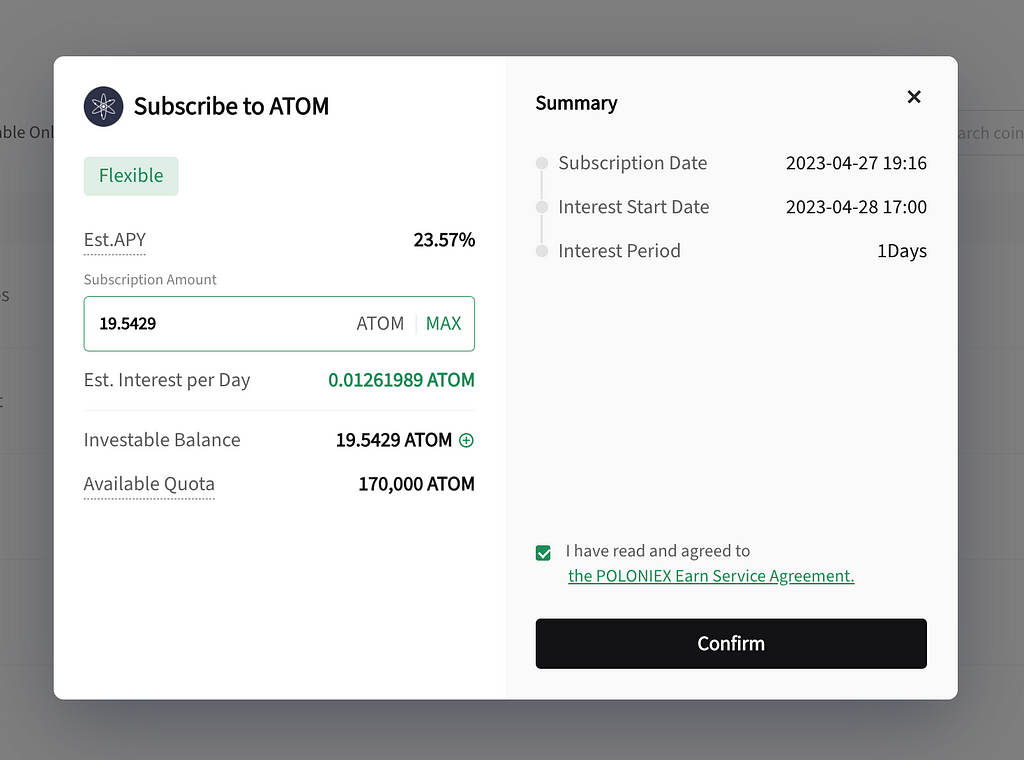
Simply input the amount you want, agree to our Terms and confirm!
was originally published in The Poloniex blog on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.

